Antiviral efficacy studies
Antiviral efficacy
We are a leading laboratory in antiviral efficacy studies for disinfectants, cosmetics, and air purifiers.
Our virus bank
- COVID-19 virus, SARS-CoV-2 (B.1.1.17), Omicron (B.1.1.529), Delta (B.1.617.2). BSL-3 Services.
- Vaccinia virus ATCC VR-157
- Human Adenovirus, Human Bocavirus, Human Coronavirus 229E, Human Coronavirus HKU1, Human Coronavirus NL63, Human Coronavirus OC43, Enterovirus, H1N1, Influenza A, Influenza B, Human Metapneumovirus A, Human Metapneumovirus B, Human Parainfluenza 1, Human Parainfluenza 2, Human Parainfluenza 3, Human Parainfluenza 4, Human Parechovirus, Human Rhinovirus, Respiratory Syncytial Virus A, Respiratory Syncytial Virus B, HCV, HBV, HIV, Dengue and Zika Virus, Hepatitis, Herpesviridae.
Our methods
- Viral titration and cytopathic effect
- Genetic material damage through RT-qPCR
- Viral replication inhibition (CALU-3 cells)
Our tests are avalible for:
 Development and validation of different types of technologies: ionization, filtration, and UVs, among others.
Development and validation of different types of technologies: ionization, filtration, and UVs, among others.
ASTM E3135-18 :Standard Practice For Determining Antimicrobial Efficacy Of Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation Against Microorganisms On Carriers With Simulated Soil.

Long-lasting, residual action, validation in dirty conditions: these are some of the tests we provide to guarantee the reliability of your development. In addition to effectiveness, we evaluated safety, irritability, and in vitro phototoxicity.
EN 14476:2013+A2:2019: Quantitative suspension test for the evaluation of virucidal activity of disinfectants intended for use in the medical area.
Evaluation of porous and non-porous surfaces according to international guidelines.
ISO 18184:2019: Determination of the antiviral activity of textile products and porous surfaces.
ISO 21702:2019: Measurement of antiviral activity on plastics and other non-porous surfaces.
What is cytophatic effect?
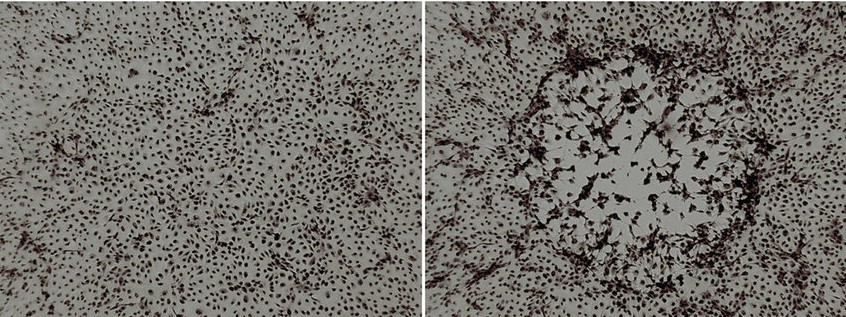
Cytopathic effect (CPE), structural changes in a host cell resulting from viral infection. CPE occurs when the infecting virus causes lysis (dissolution) of the host cell or when the cell dies without lysis because of its inability to reproduce.
How to measure virus viability?
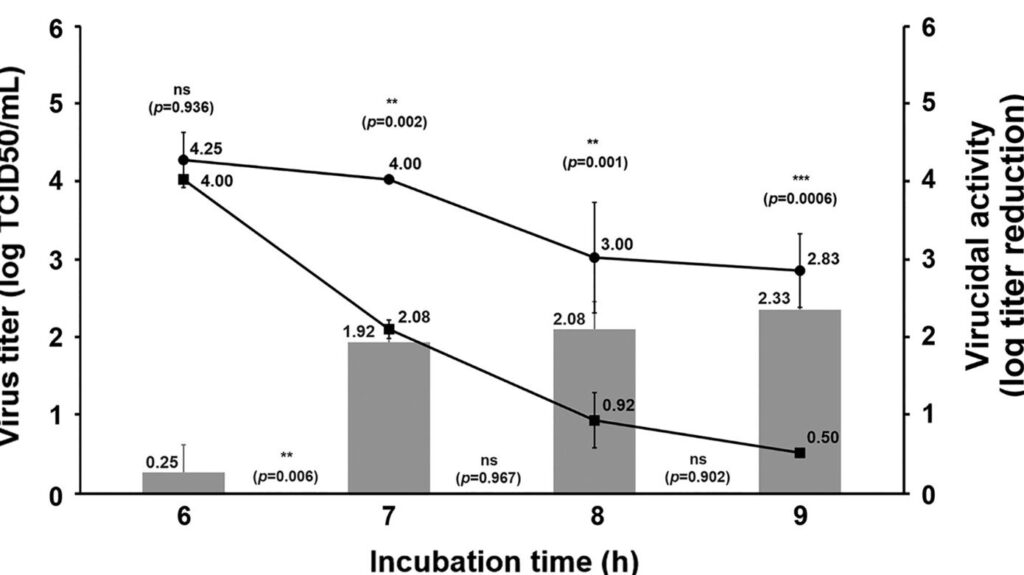
TCID50 (Median Tissue Culture Infectious Dose) assay is one method used to verify the viral titer of a testing virus. Host tissue cells are cultured on a well plate titer, and then varying dilutions of the testing viral fluid are added to the wells.
